IOT
фото
The Internet of Things (IoT) is but one of the phrases bandied about to characterize the advanced connectivity of devices, systems and services that goes beyond machine-to-machine (M2M) communications. It covers a variety of protocols, domains and applications. In addition to IoT, there’s the Industrial Internet, the Internet of Everything and variations on each as the concept continues its creep into the branding realm.
IoT enables freight and passenger roads to use sensors, software M2M learning, “Big Data” analytics, cloud computing and other technology to gather and analyze information from various sources and data streams — and then use those analyses to drive efficiencies, better manage operations and, possibly, offer new services.
IoT, then, represents a world of opportunity for railroads and the technology providers that serve them. And it’s a world strategists in all railroad departments — from information technology (IT) to transportation to engineering to mechanical to communication and signaling — will need to tap into and be engaged with as the digital evolution continues.
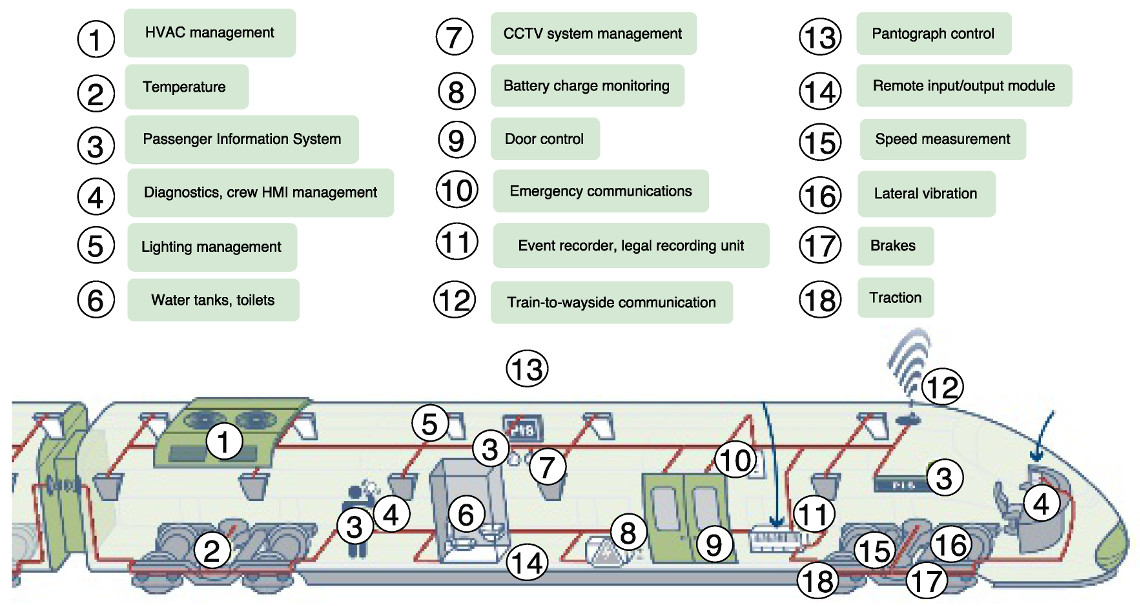
There are five ways in which IoT will redefine the railways bringing in increased efficiency and enhanced passenger experience:
1. Greater Reliability and Safety
A train that suddenly breaks down on the track can ruin the day of its passengers, lead to delays across the network, and essentially throw the entire system off-gear. However, recent developments in preventive maintenance practices prompted by IoT can help to revive the reliability of even the oldest assets. By integrating IoT sensors crucial components like brakes, wheelsets, and engines, trains become more sensitive to their operations for more efficiency.
Maintenance of rail tracks also benefits from IoT. By deploying sensors across track systems, operators can be on top of track stress and conditions, temperatures, and other variables that have predictive values for maintenance teams. If problems with wagons and tracks can be identified proactively, the operators can take pre-emptive actions for safer operations.
2. Fewer Maintenance Delays
Undesirable downtime due to sudden repairs can soon be a thing of the past. Predictive and preventive maintenance is feasible and more effective in the IoT era. Smart sensors and analytics across the train engine, coaches, and tracks allow rail systems to be remotely checked and repaired before a small issue magnifies into huge trouble. Asset health monitoring through IoT insights implies less of maintenance delays and helps in extending the life of rail infrastructure.
3. Advanced Analytics for Streamlined Operations
The operators can control their trains more efficiently by tracking them across networks and processing the data using analytics. IoT can also be employed to check the flow of passengers—those waiting at the stations, traveling in each train coach, and the times when the passenger flow is the highest. Analytics on such data can guide operators on optimization of travel schedules as per commuters’ needs and demands.
4. Restructured and Optimized Passenger Experience
IoT can help operators personalize the travel experience for individual passengers. For instance, services can be priced differently for different travelers as per the frequency of their traveling. Rail operators can enjoy greater passenger loyalty using IoT systems to understand customer experience history and make improvements for a more comfortable and convenient journey.
5. Better Product Development in the Industry
Conventional engineering solutions were not devised to support systems of systems. There can be delays and constraints in production when the process entails developing a requirements definition and then following it up with design, build, and tests. The actual feedback on product quality comes only later through customer’s complaints.
Feedback is an inherent part of operation with the Internet of Things concept. Engineers can use analytics with operations and performance data to derive valuable, actionable insights. This helps them understand the experience of customers dynamically and enhance operational quality sooner than in traditional methods.
